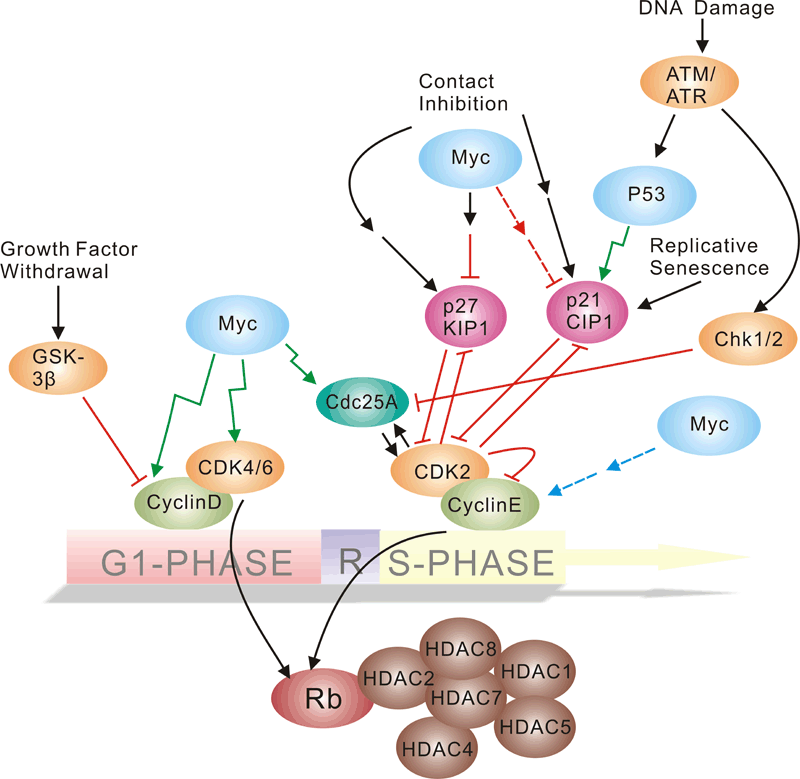
Pathway description:
Cell-division control affects many aspects of development. Caenorhabditis elegans cell-cycle genes have been identified over the past decade, including at least two distinct Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs), their cyclin partners, positive and negative regulators, and downstream targets. The balance between CDK activation and inactivation determines whether cells proceed through G1 into S phase, and from G2 to M, through regulatory mechanisms that are conserved in more complex eukaryotes. Many different stimuli exert checkpoint control including TGF, DNA damage, contact inhibition, replicative senescence, and growth factor withdrawal. G1 phase CDKs and their inhibitors (CKIs) are central to the pathways that regulate commitment to cellular division in response to positive as well as negative growth effectors. Many checkpoints are deregulated in oncogenesis, and this is often due to alterations in cyclin-CDK complexes.CDK activity is modulated by cyclin binding, phosphorylation, and CKIs, including the INK4 proteins and the closely related inhibitors p21Cip1 and p27Kip1. The downstream targets of CDKs and their modulation by TGF-beta and other growth factors include proteins of the retinoblastoma family, and the related modulation of the transcriptional activity of the E2F family members.
Selected Reviews:
Dyson, N. (1998) The regulation of E2F by pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev. 12, 2245–2262.
Ravitz MJ, Wenner CE. (1997)Cyclin-dependent kinase regulation during G1 phase and cell cycle regulation by TGF-beta. Adv Cancer Res. 71:165-207.
van den Heuvel S.(2005) Cell-cycle regulation. WormBook. 21:1-16.