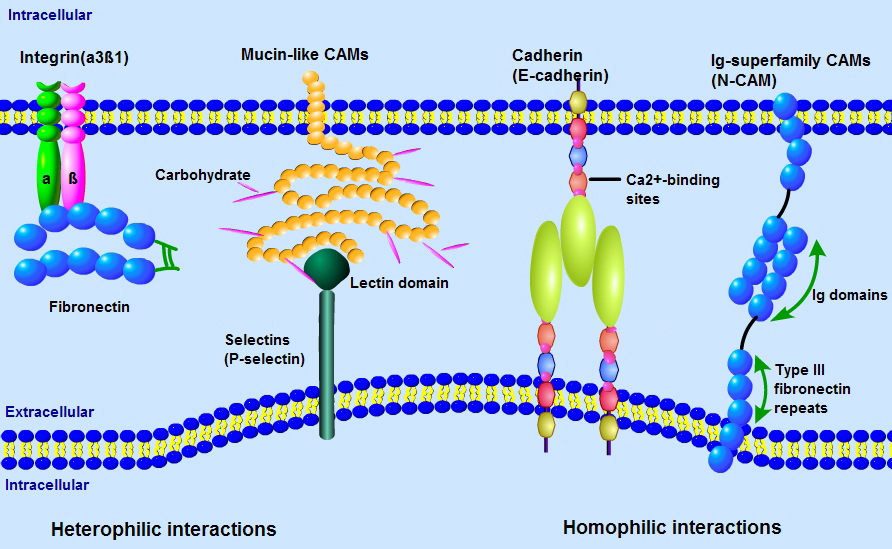
Adhesion Molecules are proteins located on the cell surface involved in binding with other cells or with the extracellular matrix (ECM) in the process of cell adhesion or cellular interactions. Essentially, adhesion molecules help cells stick to each other and to their surroundings. Adhesion Molecules include Integrins, Ig superfamily Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMS), Cadherins, Lectins, and others. These proteins are typically transmembrane receptors and are composed of three domains: an intracellular domain that interacts with the cytoskeleton , a transmembrane domain, and an extracellular domain.
Adhesion molecules play critical roles in a variety of biological processes. For instance, one important part adhesion molecules serve in the immune system is to enhance pairing between many less avid receptors and their ligands and transmit signals that direct specific effecter functions during an inflammatory response. In development they play key roles in tissue morphogenesis, cell migration, and axon guidance. Pathologically, adhesion molecules have been discovered to play a critical role in tumor cell invasiveness and metastases.
Selected Reviews:
Angst B. (2001)The cadherin superfamily: diversity in form and function. J Cell Sci. 114 (Pt 4): 629-41
Zetter BR. (1993) Adhesion molecules in tumor metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 4(4):219-29.
Hulpiau P. (2009)Molecular evolution of the cadherin superfamily. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.. 41 (2): 349-69.
Ikeda H. (1998) Cell adhesion molecule. Nippon Rinsho. 56(10):2493-9.


