产品名称Rat IL-1α ELISA kit
简述ELISA Kit
应用ELISA
种属反应性Rt
特异性Natural and recombinant Rat IL-1α Ligand
交叉反应性No significant interference observed with available related molecules.
基因/蛋白名称Rat IL-1α
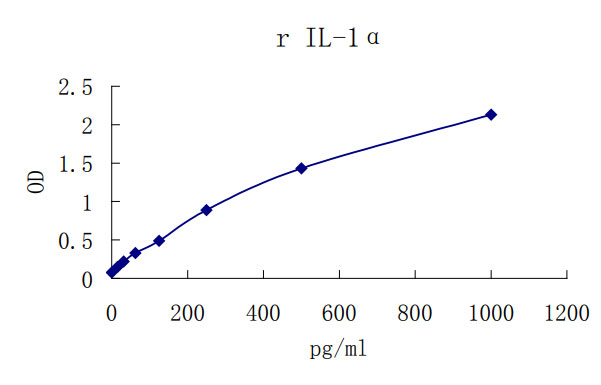
Sensitivity: 7pg/mL
Sample Type: Cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin)
Sample Volume: 20 uL
Assay Time: 3 hour
Detection method: Colorimetric
- Aluminium pouches with a Microwell Plate coated with monoclonal antibody to rat IL-1α (8X12)
- 2 vials rat IL-1α Standard lyophilized, 1000 pg/ml upon reconstitution
- 2 vials concentrated Biotin-Conjugate anti-rat IL-1α antibody
- 2 vials Streptavidin-HRP solution
- 1 bottle Standard /sample Diluent
- 1 bottle Biotin-Conjugate antibody Diluent
- 1 bottle Streptavidin-HRP Diluent
- 1 bottle Wash Buffer Concentrate 20x (PBS with 1% Tween-20)
- 1 vial Substrate Solution
- 1 vial Stop Solution
- 4 pieces Adhesive Films
- package insert
Interleukin-1α (IL-1α, also known as IL-1F1) and IL-1β (IL-1F2) are pleiotropic cytokines that belong to the IL-1 gene family. IL-1α and IL-1β bind to the same cell surface receptors and share biological functions. The two proteins have approximately 23% amino acid (aa) sequence homology and both are synthesized as 31 kDa precursors that lack hydrophobic signal peptide sequences. Current evidence suggests that IL-1 proteins may be secreted via non-classical pathways (1-4).
Rat IL-1α cDNA encodes a 270 aa residue pro-IL-1α precursor (5). The 114 aa pro-region contains a nuclear localization sequence, a lysine-based myristoylation site, one phosphorylation site, and one potential N-linked glycosylation site (5-8). The 156 aa mature region contains no cysteines and one potential N-linked glycosylation site (5). Pro-IL-1α is primarily localized to the cytosol after synthesis. It is known to translocate to the nucleus after cell activation and initiate gene transcription (9, 10). Some IL-1α is released extracellularly and exists as either a membrane-bound form or as a circulating 17 kDa molecule. When membranebound, membrane association is mediated either via a poorly-understood cell surface lectin interaction with the glycosylated IL-1α pro-form, or by interaction of myristoylated pro-IL-1α with plasma membrane phospho-lipids (8, 11-13). When released as a 17 kDa soluble form, calpain initiates cleavage of the pro-IL-1α precursor (14). Unlike pro-IL-1β, which is biologically inactive, both pro-IL-1α and mature IL-1α have been shown to be biologically active (15, 16). Within the mature protein, rat IL-1α shares 79%, 60%, 59%, 58%, 57%, and 56% aa sequence identity with mouse, rabbit, human, bovine, canine and feline proteins, respectively (17-21). Mammalian cells known to express IL-1α include brown adipocytes (22), keratinocytes (23), monocytes (24), macrophages (25), endothelial and smooth muscle cells (26), mast cells (27), Schwann cells (28), as well as osteoblasts and osteoclasts (29).
Three type I transmembrane immunoglobulin superfamily proteins, IL-1 receptor type I (IL-1 R1), IL-1 receptor type II (IL-1 R2), and IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1 RAcP, IL-1 R3)are involved in the formation of high affinity cell surface IL-1 receptor complexes. Both IL-1 R1 and IL-1 R2 can bind directly to IL-1α. IL-1 RAcP does not bind IL-1α directly, but interacts with IL-1 R1 in the presence of IL-1 to form the high-affinity receptor complex which is required for intracellular signal transduction. IL-1 RAcP also interacts with IL-1 R2 to form a non-functional high-affinity receptor complex that does not transduce IL-1 signals. Therefore, IL-1 R2 functions as a decoy receptor that attenuates IL-1α functions (16, 30, 31).
IL-1α possesses a wide variety of biological activities and plays a central role in mediating immune and inflammatory responses. Normal production of IL-1α is critical for hematopoiesis, angiogenesis, osteoclast differentiation, and initiation of normal host responses to injury and infection(15,32-34). Inappropriate production of IL-1α has been implicated in the production of a variety of pathological conditions including sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and atherosclerosis (1, 13, 15).
Arend, W.P. (2002) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13:323.
Sims, J.E. et al. (2001) Trends Immunol. 22:536.
Nickel, W. (2003) Eur. J. Biochem. 270:2109.
Dinarello, C.A. (1991) Blood 77:1627.
Nishida, T. et al. (1989) J. Biochem. 105 :351.
Wessendorf, J.H.M. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:22100.
Beuscher, H.U. et al. (1988) J. Biol. Chem. 263:4023.
Stevenson, F.T. et al. (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:7245.
Werman, A. et al. (2004) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:2434.
Pollock, A.S. et al. (2003) FASEB J. 17:203.
Kaplanski, G. et al. (1994) Blood 84:4242.
Brody, D.T. and S.K. Durum (1989) J. Immunol. 143:1183.
Apte, R.N. and E. Voronov (2002) Semin. Cancer Biol. 12:277.
Kobayashi, Y. et al. (1990) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:5548.
Dinarello, C.A. (1996) Blood 87:2095.
Boutin, H. et al. (2003) Mol. Neurobiol. 27:239.
Lomedico, P.T. et al. (1984) Nature 312:458.
Furutani, Y. et al. (1985) Nucleic Acids Res. 13:5869.
March, C.J. et al. (1985) Nature 315:641.
Leong, S.R. et al. (1988) Nucleic Acids Res. 16:9053.
Straubinger, A.F. et al. (1999) Gene 236 :273.
Burysek, L. and J. Houstek (1996) Cytokine 8:460.
Takei, T. et al. (1998) J. Cell. Biochem. 69:95.
Okubo, Y. and M. Koga (1998) J. Dermatol. Sci. 17:223.
Hernandez-Pando, R. et al. (1997) Immunology 90:607.
Lundberg, I.E. and P. Nyberg (1998) Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 10:521.
Lin, T-J. et al. (2002) J. Immunol. 169:4522.
Skundric, D.S. et al. (2001) J. Neuroimmunol. 116:74.
Lossdorfer, S. et al. (2002) Cytokine 20:7.
Sims, J.E. (2002) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 14:117.
Martin, M.U. and H. Wesche (2002) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1592:265.
Vidal, O.N.A. et al. (1998) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 248:696.
Murphy, J-E. et al. (2000) J. Invest. Dermatol. 114:602.
Ristimaki, A. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:8413.
如果您使用该产品EK0525发表了文章,请通知我们,让我们可以引用您的文献。




 1-2周
1-2周

